H.E.S.S.
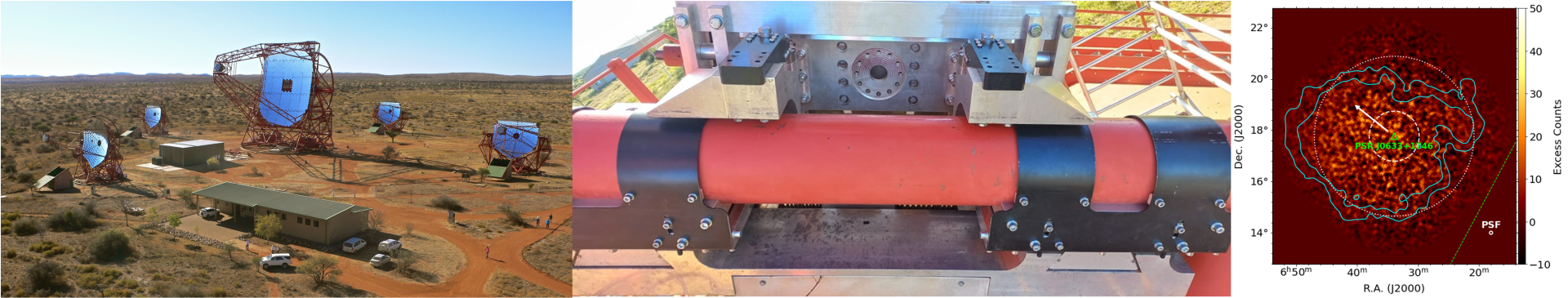
Although ground-based gamma-ray astronomy began in the 1950s, it is only recently that it has developed the methods that have made it a discipline in its own right. Very high-energy gamma rays (100 GeV to 10 TeV) from the cosmos interact in the atmosphere to produce an electromagnetic shower that is detected by its emission of Cherenkov radiation. This light is focused by telescopes onto their cameras, which are made up of several hundred photomultipliers.
With the H.E.S.S. (High Energy Stereoscopic System), MAGIC and VERITAS experiments since 2000 and the entry into operation of the large H.E.S.S.-2 telescope in 2012, ground-based gamma-ray astronomy is currently undergoing a period of intense activity. In ten years, the number of TeV sources has increased by a factor of 20, with more than a hundred referenced sources.
The vast majority are associated with galactic objects (neutron stars, black holes, supernova remnants) as well as extragalactic objects (blazars, radio galaxies).

Activities du LAPP
The LAPP group has been engaged on the H.E.S.S. experiment from 2007 to 2022. The technical commitment for the H.E.S.S. II telescope was to provide an automatic system for :
Fix and lock the camera in the nose of the telescope, with the possibility of adjusting the focus to a maximum distance of 20 cm.
Position or remove the camera from the telescope (loading/unloading system) and replace it with a clone of identical size, weight and centre of gravity to the camera.
This project comprised two sub-projects, closely combining mechanical, automation and IT aspects: the autofocus system (figure 3) and the unloading and transfer trolleys.
The group decided to withdraw from the HESS experiment in order to devote itself entirely to the CTA project, focusing on the LST telescopes from both a technical and data analysis point of view.
Completed Phd thesis and Habilitations
- Mathieu De Bony de Lavergne – Phd’s defense – feb. 28, 2023 – Gamma-Ray Bursts observations with Cherenkov telescopes: H.E.S.S. legacy observations and optimisation of follow-up and detection with the Large-Sized Telescopes of CTA
- Celine Armand – Phd’s defense – nov. 18, 2020 – Dark matter searches in the direction of dwarf galaxies with H.E.S.S. and characterization of the gamma-ray emission from the Galactic center and Andromeda galaxy with Fermi-LAT
- Quentin Piel – Phd’s defense – July 5, 2019 – Commissioning of the first CTA large size telescope and study of transient gamma-ray sources
Collaboration
The H.E.S.S. collaboration involves more than 260 scientists from around 40 scientific institutions and 13 different countries. In France, the CNRS and the CEA are the organisations most involved, with nine laboratories, including 7 at IN2P3.
Actualités
- All
- Science

In June 2002, the H.E.S.S. collaboration directed its first telescope towards Blazar PKS 2155-304, one of the brightest active galactic

In Namibia, the telescopes of the H.E.S.S. experiment, to which the LAPP contributes, have been indirectly detecting cosmic radiation

After ten years of effort, a collaboration of scientists, including LAPP, observed for the first time the emission of


